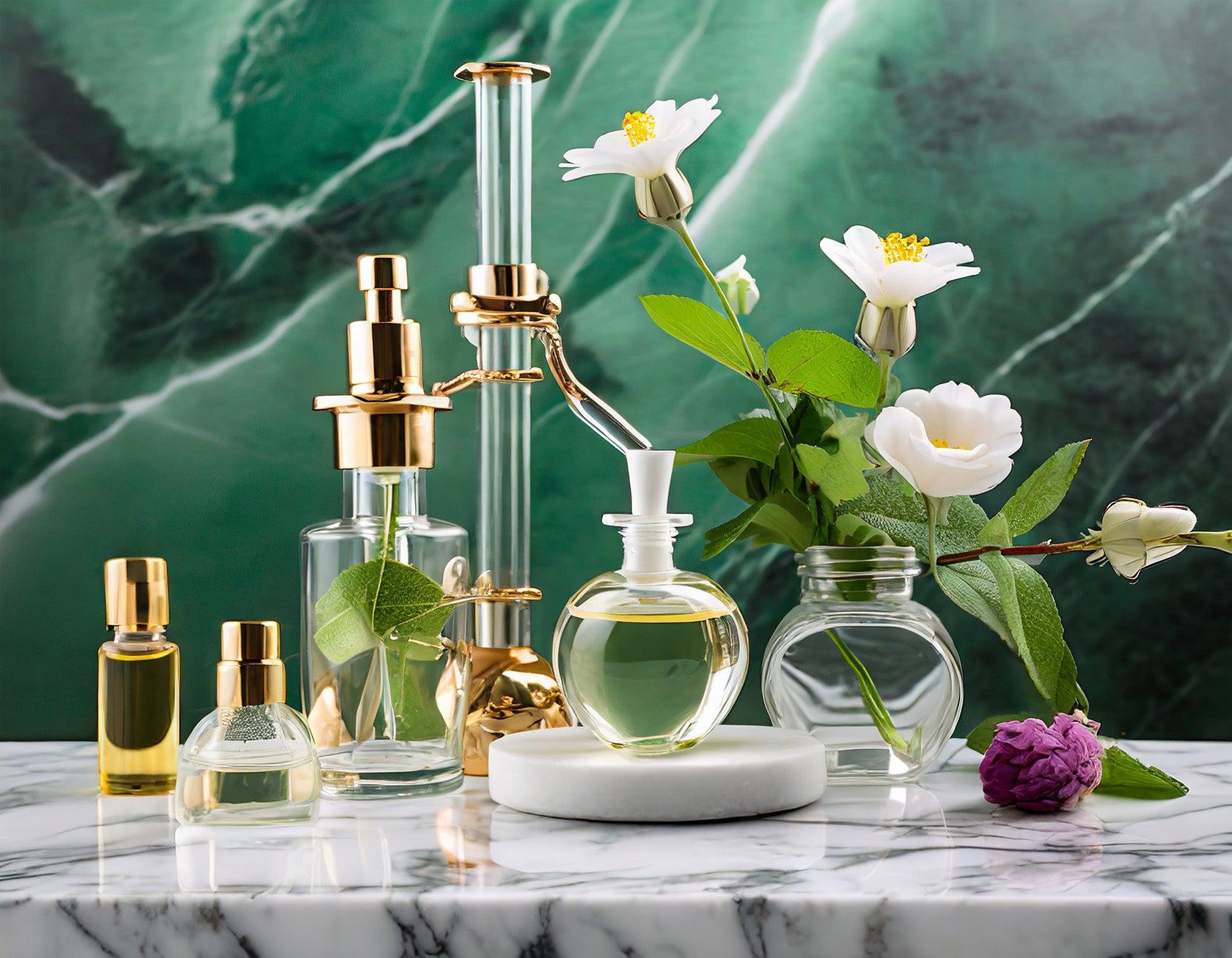
Methods of Perfume extraction from flowers depends on the type of flower and the specific fragrance compounds you want to extract. There are several methods commonly used in the perfume industry for those interested in natural perfume, and each has its advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the most common methods:
- Steam Distillation perfume extraction:
Steam distillation is the most widely used method for extracting essential oils from flowers. In this process, steam is passed through the flower material, causing the volatile aroma compounds to evaporate. The steam and essential oil vapor are then condensed and collected separately. This method is suitable for flowers like lavender, tagetes and geranium.
- Solvent Extraction perfume extraction:
Solvent extraction involves using a solvent (typically hexane or ethanol) to dissolve the aromatic compounds from the flower material. The solvent is then separated from the extract, leaving behind the concentrated fragrance oil. This method is often used for delicate flowers like rose, jasmine and tuberose.
- Enfleurage perfume extraction: :
Enfleurage is an old and labour-intensive method that involves placing flower petals on a layer of odourless fat, such as lard or vegetable oil. Over time, the fat absorbs the aroma compounds from the flowers. The fat is then washed with alcohol to separate the fragrance compounds, creating an absolute or pomade.
- Supercritical Fluid perfume extraction
Supercritical fluid extraction uses carbon dioxide in a supercritical state as a solvent to extract fragrance compounds from flowers. This method is relatively new and efficient, producing high-quality essential oils.
- Maceration perfume extraction:
Maceration involves soaking flower materials in a carrier oil to extract the fragrance. This is a simple method, but it can take several weeks or even months for the oil to become saturated with the aroma compounds.

Steam distillation perfume extraction:
Steam distillation perfume extraction is a widely used method for extracting essential oils from various plant materials, including flowers. The benefits of steam distillation for flower oils include:
- Preservation of Aromatic Compounds:
Steam distillation is an efficient method that helps preserve the delicate aromatic compounds present in some flowers. This results in high-quality essential oils with the true and characteristic scent of the flower. - Solvent-Free Extraction:
Steam distillation is a solvent-free extraction method free from hexane contamination, making it a preferred choice for producing natural and organic essential oils. This is the single most important reason why it is a safe economical way, however steam distillation are for all flowers - Separation of Essential Oil and Hydrosol:
Steam distillation also produces a co-product called hydrosol (or floral water), which has its own set of uses and benefits. This co-product can be collected and used alongside the essential oil. - Versatility:
Steam distillation can be applied to a wide range of flowers and plant materials, making it suitable for extracting essential oils from many different botanical sources.
Many flowers are not suitable for steam distillation but here are some that are suitable for steam distillation to produce essential oils include: lavender, chamomile, neroli, ylang ylang, geranium, clary sage.

Solvent perfume extraction absolute oil
Solvent perfume extraction, specifically the production of absolute oils, is commonly used for flower extraction like jasmine, jonquil, tuberose and rose because it offers unique advantages and is especially well-suited for extracting the fragrant constituents from flowers. However, it also comes with certain limitations and challenges. Let’s discuss the strengths and weaknesses of solvent extraction in the context of absolute oil production from flowers:
Strengths of Solvent perfume Extraction for Absolute Oil Production:
- Efficient Extraction of Fragrance: Solvent extraction, particularly for absolute oils, is highly efficient at capturing and preserving the delicate and complex fragrance compounds found in flowers. This method can yield a rich and true representation of the flower’s aroma.
- High Oil Yield: Absolute oil production often results in a high yield of essential oil, making it a cost-effective choice for extracting the fragrance components of flowers.
- Extraction of Fragile Components: Solvent extraction is gentle on fragile, heat-sensitive compounds, allowing for the capture of a broader range of aromatic molecules that may be altered or lost with other extraction methods.
- Ability to Work with Fragile Flowers: Solvent extraction is ideal for flowers that are too delicate or have low oil content, as it minimizes the risk of damaging the flower material during the extraction process.
- Selective Extraction: By adjusting the choice of solvent and extraction conditions, it’s possible to selectively extract specific aromatic compounds, tailoring the absolute oil to have particular scent profiles or therapeutic properties.
- Consistency and Purity: Solvent extraction can provide a consistent and pure product, ensuring that the fragrance and chemical composition are maintained from batch to batch.
Weaknesses of Solvent perfume Extraction for Absolute Oil Production:
- Residual Solvents: A significant concern with solvent extraction, including for absolute oils, is the potential presence of residual solvents in the final product. Stringent purification steps are necessary to remove all traces of solvents to ensure product safety and quality. Quality supplier must guarantee 1 parts per million residue in their documentations. If the smell has hints of petroleum then the product has not been thoroughly purified.
- Environmental and Health Concerns: The use of chemical solvents, such as hexane, can raise environmental and health concerns. Proper handling, disposal, and regulatory compliance are essential to mitigate negative impacts.
- Quality Control and Standardization: Ensuring consistent quality and adherence to regulatory standards can be challenging, as variations in solvent quality and extraction conditions can affect the final product.
- Cost: Solvent extraction can be expensive due to the need for specialized equipment, safety measures, and solvent handling. Additionally, the need for careful purification can add to production costs.
- Time-Consuming Process: The production of absolute oils through solvent extraction can be a time-consuming process, especially when purification steps are taken into account.
- Alteration of Natural Scent: Depending on the choice of solvent and extraction conditions, there’s a risk of altering the natural scent of the flower. While this can be desirable for certain applications, it may not always capture the exact scent of the fresh flower.

Enfleurage perfume extraction
Enfleurage is an age-old method for extracting the aromatic compounds from flowers like rose, tuberose and jasmine, primarily used in the production of flower absolute oils. It has evolved over time, with modern methods incorporating improvements to enhance efficiency and safety. Let’s discuss the old and modern methods of enfleurage:
Old (Traditional) Enfleurage perfume extraction:
- Cold Fat Enfleurage: This traditional method involves spreading a layer of odourless, semi-solid fat (such as lard or tallow) onto a glass or wooden frame called a “chassis.” Freshly picked flowers are gently pressed into the fat, and the process is repeated with new flowers until the fat is saturated with fragrance. This process could take several days to several weeks.
- Changing Flowers: Flowers are replaced regularly to ensure a continuous extraction of fragrance. As the fat becomes saturated with aromatic compounds, it is scraped off, and fresh fat is added. This process is repeated until the desired concentration of fragrance is achieved.
- Manual Labour: Traditional enfleurage requires significant manual labour, as flowers need to be replaced and the fat scraped off the chassis regularly. It was a time-consuming and labour-intensive process, particularly for large-scale production.
- Fragile Flower Compatibility: Enfleurage is most suitable for extracting fragrances from delicate and highly aromatic flowers, such as jasmine, tuberose, and gardenia, which would be damaged or lose their fragrance using other extraction methods like distillation.

Modern Enfleurage perfume extraction
Modern enfleurage with coconut oil is a technique commonly used in Tahiti for extracting the fragrant compounds from the delicate and highly aromatic Tiare (Gardenia tahitensis) flowers, which are native to the region. This method is also known as “enfleurage à la noix de coco.” Here is an overview of how modern enfleurage with coconut oil is employed in Tahiti:
- Choice of Medium:
In this method, coconut oil is used as the medium for enfleurage. The choice of coconut oil is influenced by its natural compatibility with the scent of Tiare flowers and its solidification at cooler temperatures, allowing for the preservation of the fragrant compounds. - Preparation of Flowers:
Freshly harvested Tiare flowers are typically used for the enfleurage process. The flowers should be free from moisture, as water can cause the coconut oil to become rancid. - Application of Coconut Oil:
Coconut oil is liquefied, and a layer of it is applied to a glass or metal plate. The coconut oil serves as a solvent, capturing the volatile aromatic compounds from the flowers. - Flower Layering:
Tiare flowers are gently placed onto the layer of coconut oil. The flowers are usually spread evenly on the surface. - Maceration Period:
The flowers are left to macerate in the coconut oil for an extended period, typically ranging from several hours to a few days. During this time, the coconut oil absorbs the fragrance of the flowers. - Replacing Flowers:
As the coconut oil becomes saturated with aromatic compounds, the flowers are removed, and fresh flowers are layered onto the coconut oil. This process is repeated multiple times to enhance the fragrance concentration. - Solvent Concentration:
After several rounds of flower replacement, the coconut oil is rich in the fragrant compounds of the Tiare flowers. The coconut oil has absorbed the unique scent of the flowers, creating a highly aromatic oil. - Filtration and Processing:
The coconut oil is filtered to remove any residual flower material, and the resulting aromatic coconut oil is then used as a fragrance or incorporated into various cosmetic products, perfumes, and skincare items. - Quality Control:
Quality control measures are implemented to ensure the purity, consistency, and safety of the aromatic coconut oil.
Modern enfleurage with coconut oil is a unique and labour-intensive method that is well-suited for preserving the delicate scent of Tiare flowers. This technique is an important part of Tahitian culture and is used to produce highly fragrant and sought-after Tiare flower absolute oil. It exemplifies the traditional art of capturing the essence of flowers in a way that pays homage to the cultural and natural heritage of the region.
Supercritical Fluid Perfume Extraction (SFE)
This is a modern and advanced method for extracting essential oils and other aromatic compounds from flowers and various plant materials. It offers several merits and advantages, but it also comes with some disadvantages. Let’s discuss both:
Merits of Supercritical Fluid Extraction for Flower Oils:
- High Selectivity: Supercritical CO2 is commonly used as the solvent in SFE. It is highly selective and can be fine-tuned to extract specific compounds, allowing for the precise extraction of desired aromatic constituents from flowers.
- Low Temperature and Pressure: SFE operates at relatively low temperatures and pressures, which helps in preserving the delicate volatile compounds found in flowers. This method minimizes the risk of thermal degradation and alteration of the extracted oils.
- Environmentally Friendly: Supercritical CO2 is considered an environmentally friendly solvent, as it is non-toxic and non-flammable. It also leaves behind no residual solvents in the extracted oil.
- High Purity: SFE typically yields highly pure essential oils because it avoids the use of chemical solvents and doesn’t introduce impurities into the final product.
- Customization: SFE allows for customization of the extraction process to target specific compounds, enabling producers to create oils with precise aromatic profiles and therapeutic properties
- Reduced Processing Time: SFE is generally a quicker extraction method compared to traditional processes like steam distillation or enfleurage, making it more efficient for large-scale production.
- Lower Energy Consumption: The lower operating temperatures in SFE lead to reduced energy consumption, contributing to cost-effectiveness.

Disadvantages of Supercritical Fluid Perfume Extraction for Flower Oils:
- High Equipment Cost: Setting up and maintaining SFE equipment can be expensive. It requires specialized machinery and expertise, which may not be accessible to small-scale producers.
- Complex Process: SFE is a complex process that involves precise control of temperature, pressure, and flow rates. Operators need specific training to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the extraction.
- Extraction of Non-Aromatic Compounds: While SFE is highly selective, it can sometimes extract non-aromatic compounds, potentially diluting the desired essential oil.
- Limited Solubility: Supercritical CO2 has limited solubility for some aromatic compounds, so it may not be suitable for all types of flowers or plant materials.
- Regulatory Compliance: SFE may be subject to regulatory requirements related to the handling of high-pressure gases, which can add to the complexity and cost of the process.
- Residual CO2 Removal: After the extraction, the CO2 must be separated from the essential oil, which can be a challenging and energy-intensive step.
Supercritical Fluid Extraction is a powerful and cleanest method for extracting flower oils especially for jasmine, lilac, elderflower, michella alba, marigold and all others suitable for steam distillation. It is worth comparing the steam distilled vs CO2 extracted. The difference for CO2 extracted is always nearly more three dimensional and near 100% true to the real flower. At Prosody London we absolutely think this is the best.
Maceration Perfume Extraction Method with Alcohol
- Selection of Flowers: Choose fresh, fragrant flowers that are suitable for the desired application. Lay your flower material on kitchen towel let it dry out for a least 3 to 6 hours. This is quite a delicate exercise, water moisture will spoil the infusion and if you allow it to dry out for too long, then you lose all the delicate scent. Every material is different and only trail and error and persistent will give you good results.
- Alcohol Selection: Ethanol, often in the form of vodka or grain alcohol, is typically used as the solvent to extract aromatic compounds and other constituents from the flowers.
- Flower-Alcohol Mixture: Place the semi dried flowers in a glass container and cover them with the chosen alcohol. The container is sealed to prevent exposure to air and light.
- Maceration Period: The sealed container is stored in a cool, dark place for an extended period, typically several weeks to several months. During this time, the alcohol absorbs the fragrance and other constituents from the flowers.
- Agitation and Monitoring: Periodic agitation or stirring of the mixture may be performed to enhance the extraction process. The container is checked regularly to monitor the progress of the maceration. You may also bring the glass container into a ultra-sonic bath, this may speed up the process and yield a more intense result, but make sure you maintain the temperature to not go beyond 30 degree Celsius.
- Filtration and Processing: Once the desired aroma intensity and extraction of valuable constituents are achieved, the macerated mixture is carefully filtered to remove the flower material.
The truth about maceration is that it will never be as intense as all the other methods, but you will achieve a tinctured scented alcohol which is interesting and subtle. It is also more successful with sun dried materials, because any presence of water will make the tincture go rancid quickly.

Conclusion
In summary, the steam distilled perfume extraction essential oil is the lowest cost and cheaper to buy but is restricted to very few flower materials. The solvent perfume extraction is the most common and versatile for delicate flowers but you really need to buy from the best supplier who will guarantee the purity and 1 parts per million trace amount of hexane.
Enfleurage perfume extraction is super rare and extremely expensive even if you can find it, but its worth hunting down some geunine gardenia oil from Tahiti. With CO2 super-critical perfume extraction, you are talking about the most outstanding quality and safety profile.
Finally for artisan perfumers, maceration perfume extraction process is fun and you might get lucky sometimes only with a lot of patience, so happy extracting.